Designing 0-1 product through systems
Overview
A deep dive into the systematic approach of designing and building products from ground zero. This case study explores the methodologies, frameworks, and practical applications of systems thinking in product development, with a focus on creating scalable and maintainable design systems.
Application Architecture
The foundation of any successful product starts with a well-thought-out architecture. Here's how we break down the application structure:
 Application shell architecture showing the relationship between key components: navigation bar, toolbar, page container, and sidepanel
Application shell architecture showing the relationship between key components: navigation bar, toolbar, page container, and sidepanel
Component System
Our component system is built with modularity and reusability in mind, implementing a consistent design language across both light and dark themes:


Component system overview showing consistent design patterns across light and dark themes
Design Tokens and Systems
The foundation of our design system is built on carefully crafted design tokens that ensure consistency and maintainability:
 Design token system showing the hierarchy of visual elements: icons, text, borders, and backgrounds
Design token system showing the hierarchy of visual elements: icons, text, borders, and backgrounds
Token Relationships
Our design tokens follow a systematic formula that considers usage, sentiment, and prominence:
 Formula-based approach to design tokens showing the relationship between different states and variations
Formula-based approach to design tokens showing the relationship between different states and variations
Collaborative Workflow
The product development process is inherently collaborative, involving multiple stakeholders:
 Contributor management interface showing role-based access and collaboration features
Contributor management interface showing role-based access and collaboration features
Data Management
Effective data management is crucial for product success. Our system implements a robust data handling interface:
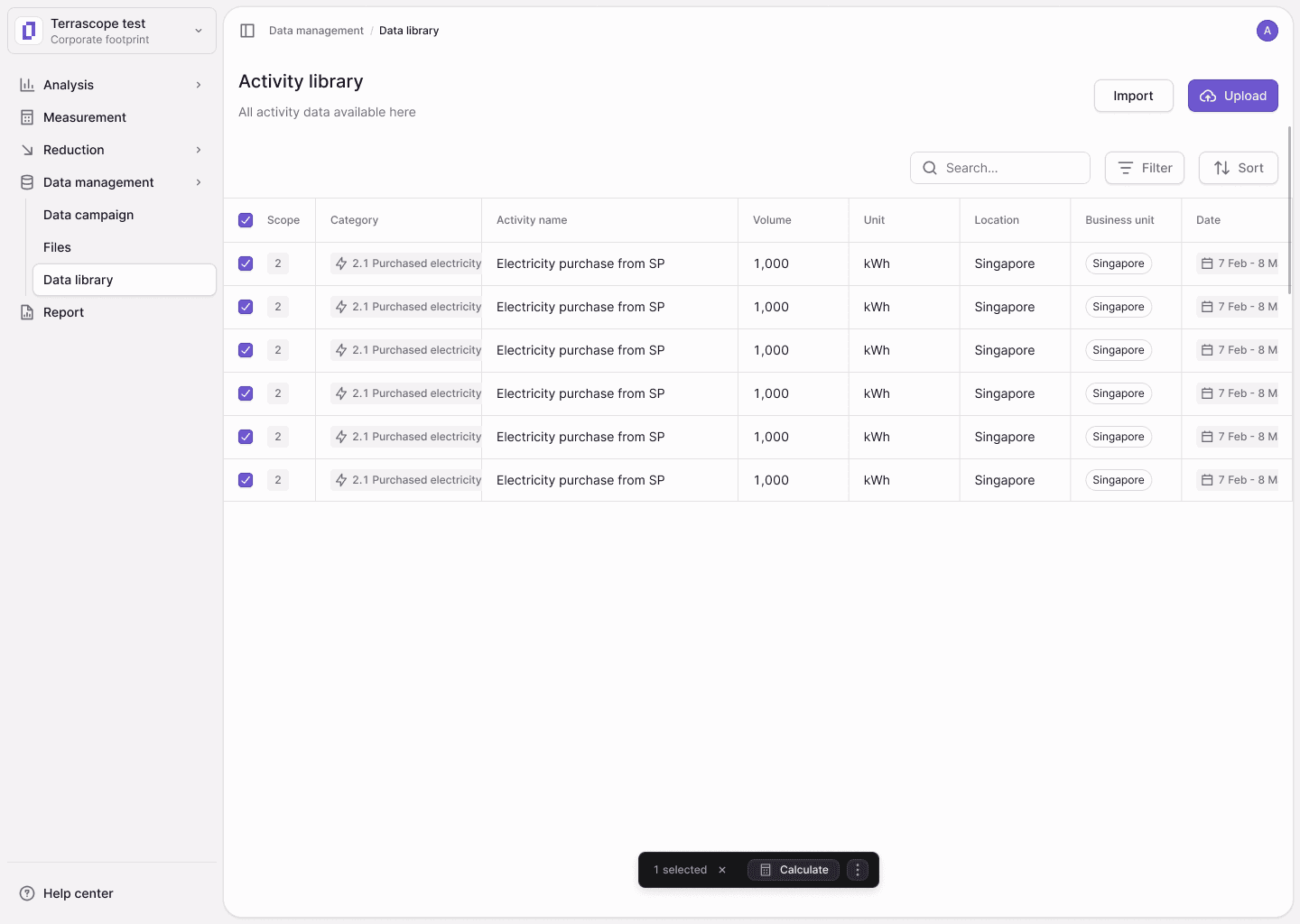 Data management workspace showing filtering, sorting, and bulk action capabilities
Data management workspace showing filtering, sorting, and bulk action capabilities
The Challenge
Building products from 0 to 1 is inherently complex and filled with uncertainties. Traditional linear approaches often fail to account for the interconnected nature of product development, leading to:
- Misaligned user expectations
- Technical debt
- Poor scalability
- Inconsistent user experiences
Systematic Approach
1. Foundation Building
The systematic approach begins with establishing solid foundations:
- User research and empathy mapping
- Market analysis and positioning
- Technical feasibility assessment
- Resource allocation planning
2. System Components
Breaking down the product into interconnected systems:
- User Interface Systems
- Technical Architecture
- Data Flow Patterns
- Feedback Loops
- Growth Mechanisms
3. Implementation Strategy
The implementation follows a systematic pattern:
-
Core System Design
- Identifying key components
- Establishing relationships
- Defining interfaces
-
Iterative Development
- Rapid prototyping
- User testing
- System refinement
-
Scale Preparation
- Performance optimization
- Scalability testing
- System monitoring
Key Insights
System Patterns
"The best products aren't just built; they're grown through carefully designed systems that enable scalable evolution."
Key patterns observed:
- Feedback loops drive iteration
- Modular systems enable flexibility
- Clear interfaces reduce complexity
- Systematic testing ensures reliability
Impact Metrics
| Aspect | Traditional Approach | Systems Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Market | 6-8 months | 3-4 months |
| User Adoption | Linear | Exponential |
| Technical Debt | High | Managed |
| Team Alignment | Variable | Consistent |
Lessons Learned
-
Start with Systems Thinking
- Map relationships early
- Identify feedback loops
- Plan for emergence
-
Design for Evolution
- Build modular components
- Create clear interfaces
- Enable easy iteration
-
Measure Systematically
- Define clear metrics
- Track system health
- Monitor user feedback
Future Considerations
The evolution of systematic product design:
- AI-enhanced system design
- Automated feedback loops
- Predictive modeling
- Enhanced visualization tools
Conclusion
Systematic approaches to 0-1 product design not only accelerate development but also create more resilient and scalable solutions. The key is understanding and leveraging the interconnected nature of product systems.